
ELECTROTHERAPY
Electrotherapy is a proven and effective form of pain management and muscle stimulation. Electrotherapy treetment involves the application of a therapeutic electrical current to the area of injury, inflammation, dysfunction, or pain.
THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS
- Reduction of painful symptoms and release of the body’s natural painkilling chemicals
- Decreasing of local swelling and inflammation
- Improvement of circulation and blood flow to accelerate the healing process
- Improvement of joint mobility
- Promotion of normal muscular tone
- Promotion of normal nervous system functioning in areas of dysfunction
INDICATIONS
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Capsulitis
- Low back pain
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Shoulder impingement syndrome
- Muscular denervation
- Muscular spasticity
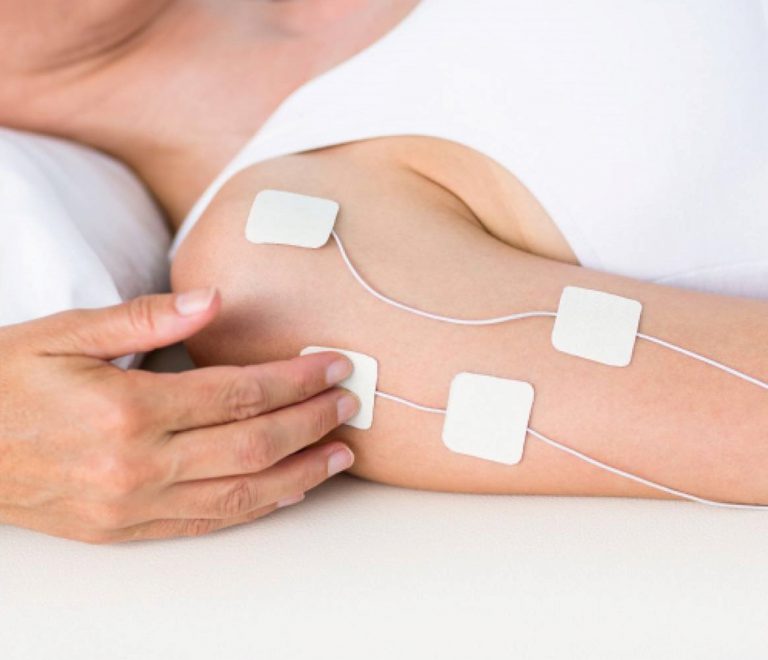
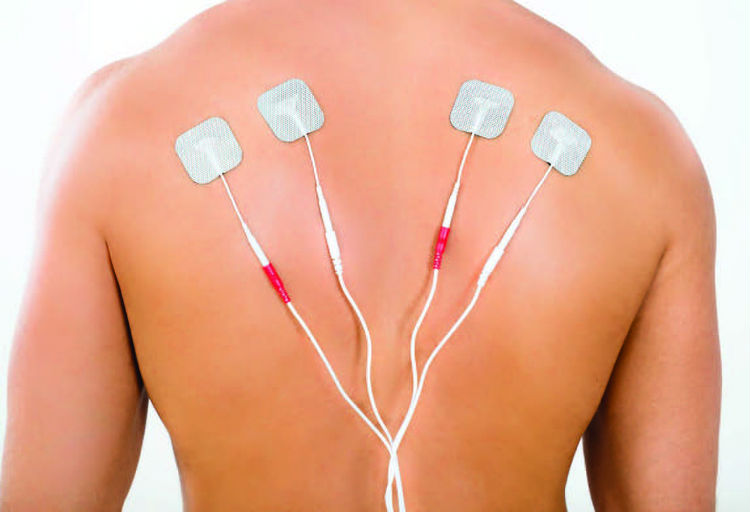
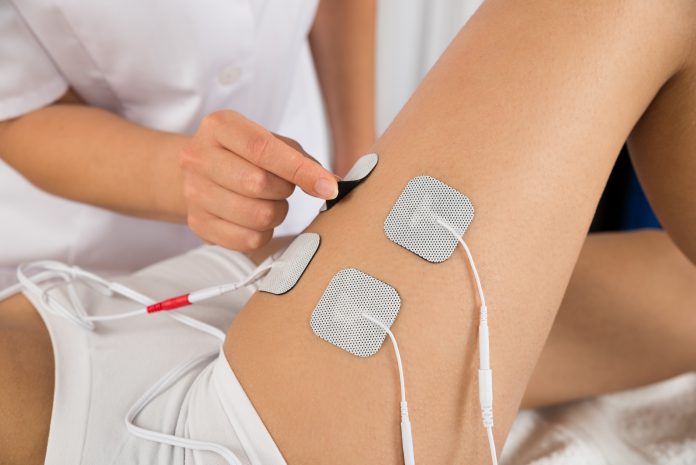
COMMON APPLICATIONS
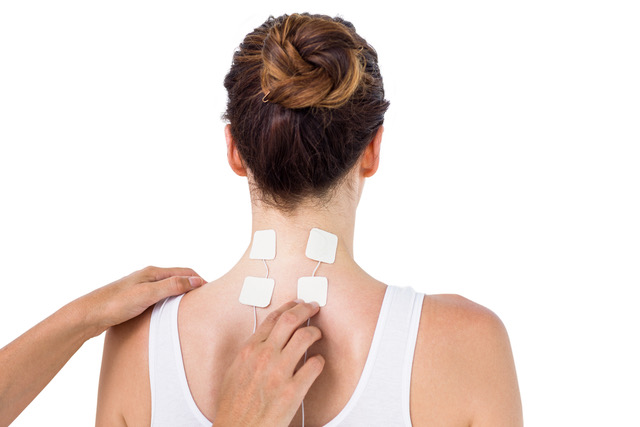

FAQ
Does the treatment hurt?
As the intensity increases, the patient will feel a tingling sensation on the skin. The most common side effect with electrotherapy is skin irritation or rash, caused by the adhesives in the electrodes or the tape holding the electrodes in place. Overusing electrotherapy may cause a burning feeling in the skin.
How many sessions will I need?
Number of treatments varies based on the indication, its severity and how the patient’s body reacts to the treatment. Number of treatments can therefore be anywhere between 6 and 12, more in very severe cases. Contact your Therapist to see how many treatments you might need.
How often will I need the treatment?
Most indications require 2–3 treatments per week which are done every second day, depending on the patient’s tolerance and their tissue response.
Are there any side-effects to the treatment?
There is a possibility of slight redness of the treated area right after the treatment which disappears within several hours after the treatment. As with most physical therapies the patient might feel a temporary worsening of their condition which also disappears within several hours after the treatment.
Are there any restrictions after the treatment?
It is recommended that patients refrain from physical activity, especially one that would involve the treated region, for about 24 hours following each treatment session.
Is there a limit to the number of treatments I can get?
No, there is no limit to the number of treatments as the therapy is non-addictive. It is up to the therapist to determine whether the patient needs more treatments or conclude that in the given patient’s case the therapy is not effective and suggest other therapy options.
